In Java you can do sorting by implementing 2 interfaces
1) Comparable
2) Comparator
Here we will see sorting example using Comparable Interface. As an example we will be sorting objects of Employee class.
When using comaprable interface make sure the object class
which you are sorting implements comaprable interface and override compareTo method correctly.
As I was more used to Java 1.4, I didnt followed any Java Generics implementation.
SortTest is main class that will actually create an array list and fill it with some random Employee objects.
Employee is class that will implement compare To method. I have added simple if-else control structure that will decide what to return on the basis of employee id.
less : -1 equal : 0 greater : 1
Here is the code for classes:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
|
import java.util.*;
public class SortTest
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
new SortTest();
}
public SortTest()
{
//fill some employee objects
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new Employee(500,“Shifoo”,150000));
list.add(new Employee(504,“Oogway”,120000));
list.add(new Employee(503,“Tigress”,100000));
list.add(new Employee(130,“Mantis”,100000));
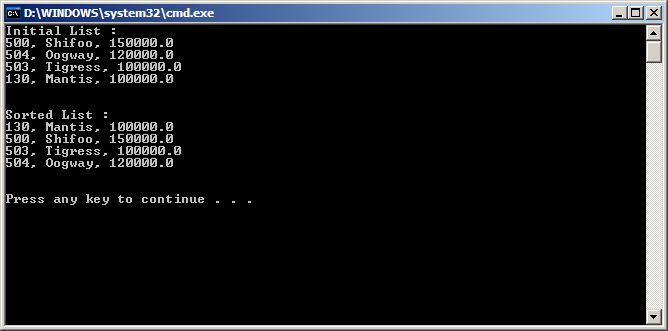
System.out.println(“Initial List :”);
print(list);
System.out.println(“n”);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(“Sorted List :”);
print(list);
System.out.println(“n”);
}
public void print(ArrayList list)
{
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
{
Employee emp = (Employee) it.next();
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
}
class Employee implements Comparable
{
public int id;
public String name;
public double salary;
public Employee(int id, String name,double salary )
{
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public int compareTo(Object object)
{
int value=0;
Employee emp = (Employee) object;
if(this.id > emp.id)
value = 1;
else if(this.id < emp.id)
value = –1;
else if(this.id == emp.id)
value = 0;
return value;
}
public String toString()
{
return this.id +“, “+this.name+“, “+this.salary;
}
}
|
- Objects should be mutally comparable. i.e you can not compare objects of different classes.
- Using comparable binds sorting to one perticular strategy.
e.g. In above example we have sorted using employee id to compare. now if we need to sort on employee name it will be difficult.
Next, I will be putting similar example using Comparator Interface.